JavaScript swap in-place array elements
November 22, 2015
No matter what sorting algorithm we are using, it’s more likely than not that we’ll need to rely on some swapping techniques, let’s explore a couple of in-place swapping helpers.
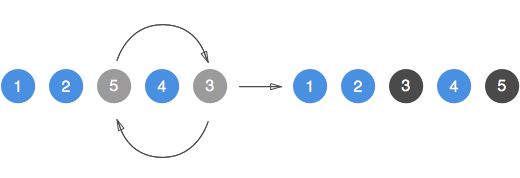
Memo swap
The memo swap technique relies on a variable to temporarily hold one of the two values that we want to swap.
function memoSwap(list, iA, iB) {
var memo = list[iA];
list[iA] = list[iB];
list[iB] = memo;
return list;
}
// memoSwap([1,2,5,4,3], 2, 4)
// -> [1,2,3,4,5]Bitwise swap - Integers only
Bitwise operators can be used to solve different problems (it’s worth reading this paper by Martin Richards, where among others things he suggests an interesting algorithm based on bitwise operators to solve the n-queens problem). A more common usage is to swap integers in place using the bitwise operator XOR (exclusive OR).
function bitwiseSwap(list, iA, iB) {
list[iA] ^= list[iB];
list[iB] ^= list[iA];
list[iA] ^= list[iB];
return list;
}
// bitwiseSwap([1,2,5,4,3], 2, 4)
// -> [1,2,3,4,5]Note: the bitwise swap method only works with integers
Swap in-place without memo
While the memo technique may look simple and to the point, sometime we just want to avoid creating an extra variable just to hold one of the values that we are going to swap. To solve this we can rely on swapping helpers that don’t need an extra variable to do their job.
function swapInPlaceWithoutMemo(list, iA, iB){
list[iB] = list[iA] + (list[iA] = list[iB]) - list[iB];
return list;
}
// swapInPlaceWithoutMemo([1,2,5,4,3], 2, 4)
// -> [1,2,3,4,5]If you wonder how the swapInPlaceWithoutMemo() function works:
the expression (list[iA] = list[iB]) does two things:
- it assigns to list[iA] the value stored at list[iB]
- returns the value stored at list[iB]
Swap in-place using Splice
We could also rely on the native splice method, to swap in place without need of a memo variable:
function swapSpliceInPlaceWithotMemo(list, iA, iB){
list[iA] = list.splice(iB, 1, list[iA])[0];
return list;
}
// swapSpliceInPlaceWithotMemo([1,2,5,4,3], 2, 4)
// -> [1,2,3,4,5]Destructuring swap - ES6 only
ES6, come with an awesome feature called destructuring assignment, that we can take advantage of for putting together an awesome in-place swapping helper function:
function destructuringSwap(list, iA, iB){
[list[iA], list[iB]] = [list[iB], list[iA]];
return list;
}
// destructuringSwap([1,2,5,4,3], 2, 4)
// -> [1,2,3,4,5]Note: the destructuring swap method only work with ES6, check compatibility or use an ES6 transpiler like babel that will compile the deconstructuring swap to a memo swap.
####Other ES6 related posts:
- ES6: JS’s Prototype-based inheritance and classes demystified
- ES6: Arrows, array-like objects and defaults
- Tail-recursive processes in JS